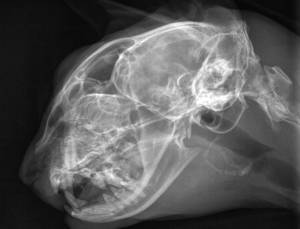
One of the most common reasons for going to the vet are problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Recently, liver disease in cats is registered more and more often. This situation is due to the fact that many food manufacturers make low-quality products, and owners want to save money on pet nutrition. But there are other causes and risk factors of hepatobiliary diseases.
Main signs of liver disease in cats
The liver is a vital organ that performs many functions:
- Detoxifying – it processes metabolites, in particular ammonia, which is formed during protein metabolism;
- It participates in digestion, produces bile;
- protein synthesis.
- Disorder of the organ leads to various disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs.
The clinical picture of liver disease depends on the etiology and pathogenesis.
- In the presence of an inflammatory process or organ replacement by connective tissue there is an increase in the liver size – hepatomegaly, sometimes joined by an increase in the spleen.
- Dyspeptic disorders are manifested by nausea, vomiting, stool disorders – both diarrhea and constipation may develop.
- Changes in the color of the mucous membranes are observed in jaundice. The pathology is classified into the following types:
- hemolytic – not associated with diseases of the parenchymatous organ, occurs as a result of massive destruction of red blood cells for various reasons;
- parenchymatous develops against the background of a pronounced damage to the structure of the liver, with the appearance of jaundice visible mucous membranes due to loss of ability of liver cells to capture free bilirubin from the blood
- Mechanical jaundice develops as a result of obstruction of bile outflow through biliary tracts, for example, in the presence of concrements or tumors in the liver or gallbladder.
- Ascites occurs when portal hypertension develops – increased pressure in the portal vein. This causes fluid to leak into the abdominal cavity and accumulate. Besides, low content of proteins-albumin in the blood contributes to formation of the pathology, which results in decreased blood oncotic pressure. The syndrome is manifested by an increase in the circumference of the cat’s abdomen, and when the animal is positioned on its hind legs, ascitic fluid drains to the lower regions, causing the abdomen to take the shape of a pear.
- Some diseases are accompanied by the development of cholestatic syndrome, which is characterized by intense itching of the skin. This symptom is caused by irritation of the skin receptors by bile acids released into the blood.
- With jaundice there is a change in the color of urine towards darker shades, and it becomes lighter in color.
- As a result of severe liver dysfunction, multiple hemorrhages on the skin develop. In severe cases, internal bleeding may occur.
Most common liver diseases in cats
The most common liver pathologies in cats include hepatitis, cirrhosis, lymphocytic, neutrophilic cholangitis, which are included in the general group of cholangitis syndrome in cats, cancer and other ailments.
Neutrophilic cholangitis
The pathology is characterized by the lesion of the bile ducts as a result of infection with pathogenic bacterial flora. Specialists suggest that the intestine becomes the source of infection, but to the end the etiology of the disease is not clear.
The disease manifests itself, as a rule, acutely – the animal repeatedly vomits, the mucous membranes and skin turn yellow, general malaise and signs of intoxication – reduced activity and appetite, a lethargic condition are observed.
Young animals are susceptible to the disease. Treatment leads to complete recovery within one to one and a half weeks. Relapses are observed in rare cases, no chronicity of the disease is characteristic.
Lymphocytic cholangitis
Unlike neutrophilic cholangitis is not associated with an infectious process. Specialists suggest that a major role in the pathogenesis of the disease plays a violation of the immune response. Most often the pathology is subjected to animals of middle and elderly age.
The autoimmune complexes formed affect the biliary passages, resulting in a gradual increase in the size of the liver, a violation of its function, the accumulation of ascetic fluid in the abdominal cavity. In the terminal stage, the pathological process involves the liver parenchyma as well. There are high risks of neutrophilic cholangitis progressing to cirrhosis.
As a rule, animals respond well to treatment, but the course of therapy takes several weeks. Recovery is often followed by relapses and the acute course of neutrophilic cholangitis becomes chronic.
Liver lipidosis
Liver lipidosis is a disease caused by deposition of lipids in hepatocytes. Fatty liver dystrophy manifests itself by dyspeptic disorders – nausea, vomiting, stool disorders develop, the animal refuses to eat for a long time. Jaundice may occur.
The severe degree of liver failure develops in the absence of adequate therapy. The cat exhibits signs of central nervous system depression – behavior changes, lethargy and increased salivary secretion are noted, and an unusual tilt of the head may occur.
The causes of the disease are unknown. In many cases, the development of the disease is preceded by hunger or stress, intestinal disease, inflammation of the pancreas.
Poisonings
Food poisoning, as well as toxic substances, can occur, for example, on a walk, when a pet eats food from the ground or from a garbage can. Intoxication by heavy metal salts, industrial compounds and other toxic substances often leads to the formation of hepatitis, cirrhosis and death of the pet.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of liver tissue in which there is no disruption of its architectonics. The etiological factor is infectious agents, as well as poisoning by toxic compounds.
Pathogenesis is infiltration of the liver by viral metabolites, bacterial products or toxins, resulting in local tissue inflammation. Massive poisoning can lead to the development of cirrhosis.
Symptomatology is usually represented by yellowing of the mucous membranes and skin, nausea, vomiting, stool disorders, and general ill health of the animal.
Hepatosis
It develops in A consequence of the accumulation of lipids in the liver. Hepatosis can occur against the background of existing pancreatitis, cholecystitis and other ailments. Most often the fatty form occurs, less often the pigmented form, in which the metabolism of bilirubin is disturbed.
The pet has dyspeptic disorders, loss of appetite and weight, and a depressed state.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease in which there is a structural disruption of the architectonics of the organ and the formation of nodules-regenerates on the background of fibrosis, that is, the replacement of parenchyma by connective tissue. The disease is characterized by a severe course, which cannot be treated. As a rule, it develops against a background of hepatitis, which can occur due to vitamin deficiency, improper nutrition, toxin poisoning, the presence of concrements in the bile-excretory ducts, helminth infestation.
Symptoms of cirrhosis in cats include signs of intoxication, loss of appetite, the appearance of ascites, jaundice. In the terminal stage, liver failure appears as a result of toxic brain damage – the animal may become aggressive, restless, disturbed gait.
Liver Cancer
Cats are susceptible to cancer. It is not uncommon for liver cancer to develop. The origin of the atypical tumor cells can originate both from the hepatocytes themselves and from the bile ducts and other structures of the liver. Most often, malignant neoplasms of the liver are metastases, and their entry is possible both hematogenously and lymphologically. The disease is characterized by a severe and lethal course.
Helminth infections
Helminth infections are a group of infectious diseases caused by parasitic worms. There are a large number of helminths that can affect the internal organs of cats. The most favorite habitat is the liver. Parasite infestation of the organ leads to the gradual destruction of its structure. Without medication, cirrhosis of the liver is formed.
Infectious diseases
Cats are susceptible to infection with the bacteria leptospira. As a result of infection, leptospirosis develops. The disease affects the liver and other internal organs. Infection occurs through contact with other animals and their biological secretions.
The clinical picture is represented by hepatomegaly, ascites, but usually there is no jaundice.
Diagnosis, treatment
When the first symptoms of liver disease in the pet should go to the veterinary clinic. The specialist first conducts an external and physical examination. At this stage, you can detect the presence of ascitic fluid, hepatomegaly, jaundice of the mucous membrane of the mouth, eyes, skin. Next, the veterinarian prescribes additional methods of examination.
- Clinical blood tests in the presence of an inflammatory reaction in the body are characterized by leukocytosis and increased sedimentation.
- Biochemical blood tests are aimed at determining the concentration of pigments, alkaline phosphatase and other criteria that may indicate the presence of liver disease.
- Abdominal radiography can reveal an increase in the size of the liver, changes in its contours, the presence of abscesses and other abnormalities.
- Ultrasound determines the structural changes of the liver with high precision, with cirrhosis and other pathologies areas of increased echogenicity may be detected. In addition, the study allows to estimate the size of the organ.
Treatment of the disease depends on the diagnosis. Determination of the timing, dosage and choice of medication is carried out by the veterinarian.
With a bacterial infection, the veterinarian prescribes a course of antibiotic therapy. The choice of drug, its dosage and duration of use is based on the type of pathogen.
If liver changes due to autoimmune processes are detected, it is advisable to prescribe glucocorticosteroids.
Cirrhosis is not amenable to drug therapy, only relief of unpleasant symptoms is possible.
Therapy of helminth infestation involves taking special medications. In severe cases, surgical intervention is possible.
An important component of treatment is diet, which helps to reduce the burden on the digestive organs and speed up the healing process.
Prevention of liver disease in cats
To avoid the occurrence of liver disease in the pet, it is necessary to monitor the diet – the menu should include all the necessary nutrients, and the portions of the amount of food should correspond to the age, breed, weight of the pet. In addition, routine vaccinations and prophylactic antihelmintic medications should be administered in a timely manner.